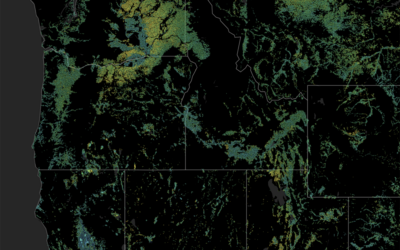
A new study published in Nature Water used satellite data spanning 38 years to examine how groundwater-dependent ecosystems (such as wetlands, meadows, and springs) in California respond to fluctuations in groundwater levels. The research can help shed light on how water management practices can best account for ecosystem needs in addition to those of human society.
A Fresh Look at the Drivers of Extreme Flooding
A new study in Science Advances finds that compounding effects of flood drivers can complicate and exacerbate the risk of extreme floods in watersheds around the world. DRI’s Guo Yu, Ph.D., assistant research professor of hydrometeorology, co-authored the research.
Meet Bea Gordon, Ph.D.
Beatrice, who also goes by “Bea,” is an interdisciplinary hydrologist with a deeply embedded concern for water availability born from her childhood on a Wyoming ranch. She is focused on working with communities in rural Nevada to understand their needs for effective climate adaptation.
New Study Reveals Impacts of Irrigation and Climate Change on Western Watersheds
DRI’s Justin Huntington coauthored the new study, led by researchers at the University of Montana and the Montana Climate Office, which published mid-December in the Nature Journal, Communications Earth and Environment.
DRI, UNLV to Partner on Regional Climate Innovation Consortium
The National Science Foundation (NSF) today announced a multi-institutional consortium – which includes UNLV and DRI – to confront the climate challenges facing the desert Southwest and spur economic development in the region.
A New, Rigorous Assessment of OpenET Accuracy for Supporting Satellite-Based Water Management
A new study offers a comprehensive multi-model, large-scale accuracy assessment of an operational satellite-based data system to compute evapotranspiration. The researchers found that OpenET data has high accuracy for assessing evapotranspiration in agricultural settings, particularly for annual crops like wheat, corn, soy, and rice.
First Dive Survey of Lake Tahoe’s Lakebed Finds High Amounts of Plastic and Other Litter
Scientists teamed up with nonprofit Clean Up the Lake to collect and analyze litter found on the bottom of Lake Tahoe. In one of the first studies to utilize scuba divers to collect litter from a lakebed, 673 plastic items were counted from just a small fraction of the lake.
Community Scientists Needed: Help Improve Winter Weather Predictions
Community members across Utah, the Great Basin, and around Lake Erie and Lake Ontario are invited to join people across the country in contributing winter weather observations. The data is collected by scientists for a NASA-funded project that seeks to improve the accuracy of winter weather predictions.
More Heatwaves and Vanishing Snow: The Lake Tahoe Basin’s Future on a Warming Planet
DRI scientists produced the most detailed projections yet for how the region’s landscape will be impacted by climate change. Lake Tahoe is known for its crystal-clear blue water, scenic mountain backdrop, and world-class recreation opportunities. Unfortunately, the lake and surrounding basin aren’t insulated from global climate change.
Meet Microplastics Research Students Angelique DePauw and Olivia Hines
Angelique DePauw and Olivia Hines are undergraduate student researchers in the Microplastics and Environmental Chemistry Lab. Together, they are conducting an experiment comparing the decomposition rates of plastic and plastic-alternative straws.