Scientists used a new technique that examines temperature records stored in bacteria to better understand the environmental conditions that may have led to the earliest human migrations into the Americas
Scientists often look to the past for clues about how Earth’s landscapes might shift under a changing climate, and for insight into the migrations of human communities through time. A new study offers both by providing, for the first time, a reconstruction of prehistoric temperatures for some of the first known North American settlements.
The study, published in Quaternary Science Reviews, uses new techniques to examine the past climate of Alaska’s Tanana Valley. With a temperature record that reaches back 14,000 years, researchers now have a glimpse into the environment that supported humans living at some of the continent’s oldest archaeological sites, where mammoth bones are preserved alongside evidence of human occupation. Reconstructing the past environment can help scientists understand the importance of the region for human migration into the Americas.
“When you think about what was happening in the Last Glacial Maximum, all these regions on Earth were super cold, with massive ice sheets, but this area was never fully glaciated,” says Jennifer Kielhofer, Ph.D., a paleoclimatologist at DRI and lead author of the study. “We’re hypothesizing that if this area was comparatively warm maybe that would have been an attractive reason to come there and settle.”
Kielhofer conducted the research during her doctoral studies at the University of Arizona, and was attracted to the Alaska location because of the wealth of research expertise being focused on the area. She also saw an opportunity to contribute to scientific understanding of a part of the world that is particularly sensitive to global climate change.
“We have to look to the past to try to better constrain how these areas have responded previously,” she said, “and how they might respond in the future under climate scenarios that we predict.”
Earlier research had relied on coarse temperature records by examining changes in vegetation and pollen. However, this information can only provide a general sense of whether a region was warming or cooling over time. To obtain a more precise history of temperatures, Kielhofer examined soil samples from the archeological sites. Using a technique known as brGDGT paleothermometry, she examined temperature records stored in bacteria to obtain a record of mean annual air temperature above freezing with a precision within about 2.8 degrees Celsius.
“Bacteria are everywhere,” she said. “That’s great because in areas where you might not have other means of recording or assessing past temperature, you have bacteria. They can preserve for millions of years, so it’s a great opportunity to look at pretty much anywhere on Earth.”
The results were surprising, she said, because many scientists had previously believed that the region experienced large swings in temperature, which may have contributed to the movement of early humans. But Kielhofer’s data showed that temperatures in the Tanana Valley remained fairly stable over time.
“The region wasn’t really responding to these global scale climate changes as we might expect,” she said. “Because temperatures are really stable through this record, we can’t necessarily use temperature as a way to explain changes in human occupation or adaptation through time, as scientists have previously tried to do.”
Kielhofer’s now turning her attention to other historical records, like changes in aridity, that could help explain how conditions in this region influenced early human communities.
###
More information: The full study, BrGDGT temperature reconstruction from interior Alaska: Assessing 14,000 years of deglacial to Holocene temperature variability and potential effects on early human settlement, is available from Quaternary Science Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2023.107979
Study authors include: Jennifer Kielhofer (DRI/University of Arizona), Jessica Tierney (Univ. of Arizona), Joshua Reuther (Museum of the North, Univ. of Alaska Fairbanks), Ben Potter and Charles Holmes (Univ. of Alaska Fairbanks), François Lanoë (Univ. of Arizona), Julie Esdale (Colorado State), Matthew Wooller and Nancy Bigelow (Univ. of Alaska Fairbanks).
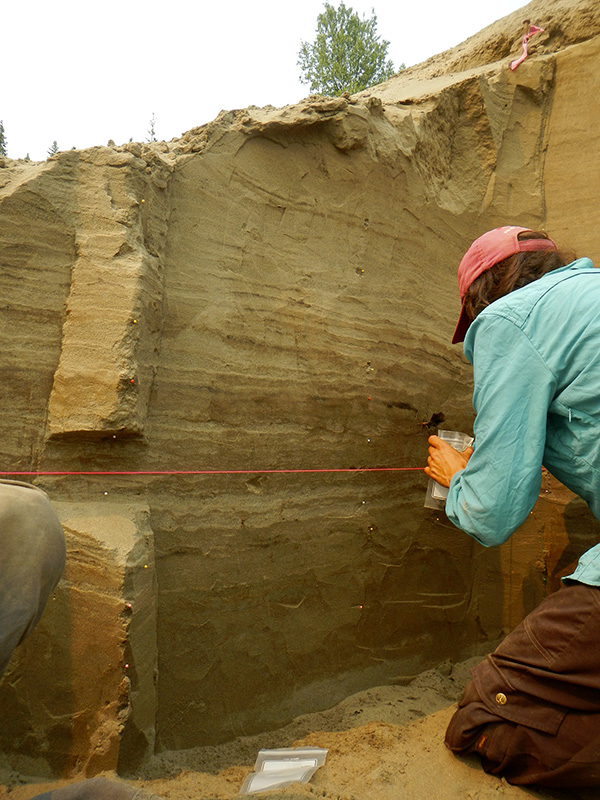

Above: Jennifer Kielhofer sampling for charcoal and biomarkers (GDGTs) at Keystone Dune in Alaska, one of the study sites as well as one of the older archaeological sites in the area (dating back ~13,000 years).