Agencies collaborate to launch wastewater surveillance dashboard
New dashboard will include COVID-19 concentration data, information about variant testing and more.
Las Vegas, Nev. (March 23, 2022) –The University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV), Southern Nevada Health District, Southern Nevada Water Authority (SNWA) and Desert Research Institute (DRI) are partnering to detect early increases of SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID) and emerging variants in Southern Nevada through wastewater surveillance. The data will be available on a new dashboard that will be updated weekly at http://empower.unlv.edu.
The wastewater surveillance program monitors SARS-CoV-2 concentrations from people who contract COVID-19 (with or without symptoms) and shed genetic material in their stools. During the COVID-19 pandemic, wastewater surveillance has tracked, monitored and provided early awareness of increases in volume of the virus as well as changes to the types of variants of COVID-19. Because people who are infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 can take several days before showing symptoms, the information provided through this surveillance program can assist with informing public health strategy and ongoing planning efforts.
In addition to being an early indicator that cases of COVID-19 may be increasing in a community, wastewater surveillance can also indicate when cases are decreasing, and the surveillance program is not dependent on people seeking testing or health care when they are sick.
“As we move into the next stage of our response to COVID-19, wastewater surveillance is going to be a powerful tool for detecting potential surges in new cases or the presence of new variants in our community. We will be able to alert the public in a timelier manner and support public health mitigation measures that can help slow the spread of the virus,” said Cassius Lockett, Director of Disease Surveillance and Control for the Health District.
Currently, the SARS-CoV-2 concentration in the wastewater of participating community water systems across Southern Nevada is tested as part of this program. Nevada was one of the first states to initiate testing, and this surveillance project represents one of the largest projects of its kind in the U.S.
“The collaboration between our community partners has enabled the collection of one of the largest and most diverse wastewater datasets in the country,” said Edwin Oh, professor and director of the Neurogenetics and Precision Medicine Lab at UNLV. “The daily and weekly analyses of these samples will help keep us one step ahead of emerging pathogens and variants.”
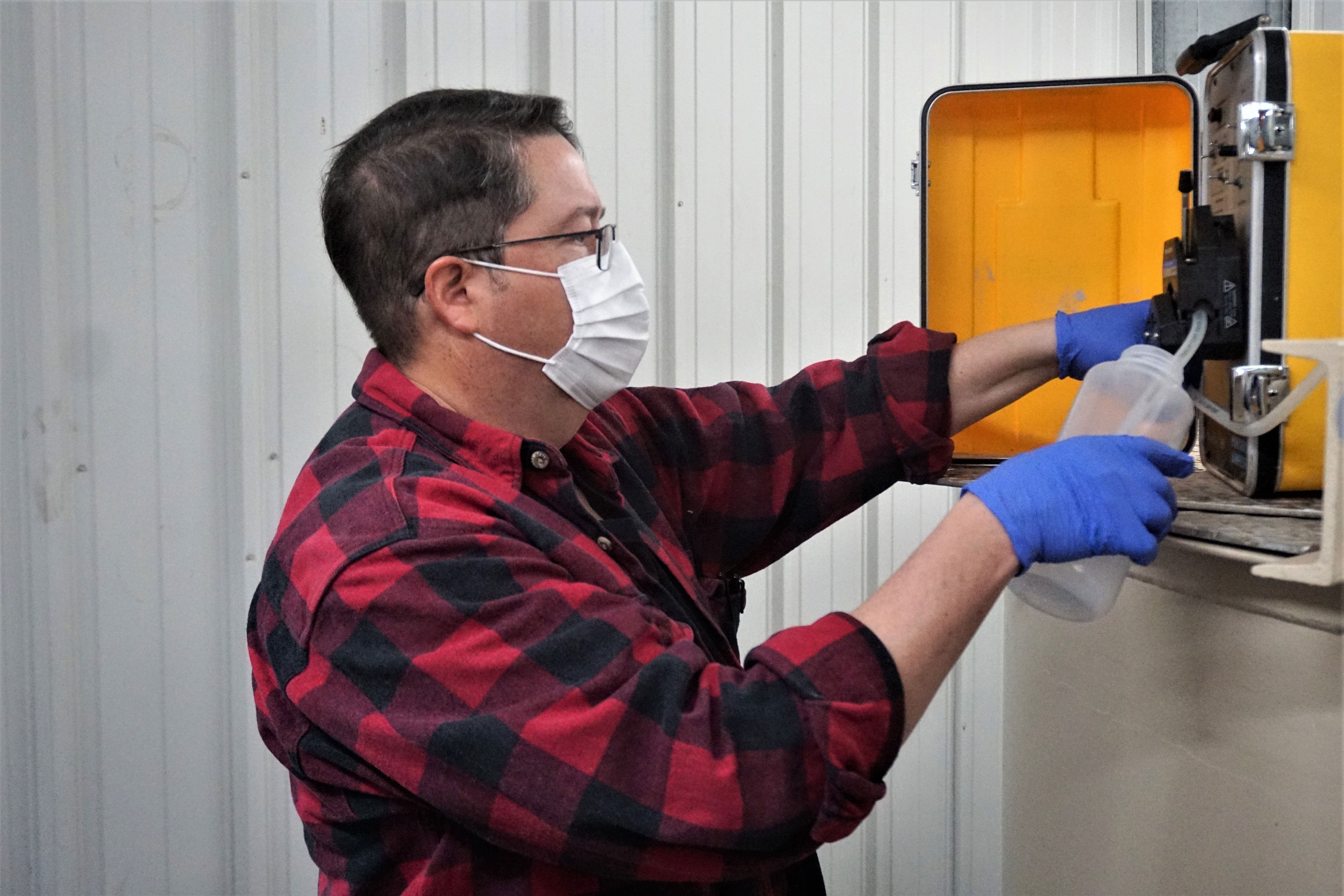

“DRI is contributing to this collaborative effort by organizing sampling from ten wastewater systems across rural Clark and Nye Counties, substantially expanding the geographic reach of the project and providing time-sensitive epidemiological data that would otherwise be lost,” said DRI Associate Research Professor of Microbiology Duane Moser. The addition of these outlying sites has a great deal to teach us about how quickly and effectively viruses spread from population centers to outlying areas with lower population densities.”
While wastewater surveillance can provide early awareness of increases in cases and potential outbreaks, the data provided cannot directly indicate the number of people who are currently infected with COVID-19. The data collected are not intended to be used as the sole method of measuring the prevalence of COVID-19 in the community. The information will be used along with other data by partner and responding agencies for planning purposes.
More information about wastewater surveillance, and national wastewater surveillance data, is available on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website at www.cdc.gov/healthywater/surveillance/wastewater-surveillance/wastewater-surveillance.html.
###
About DRI
The Desert Research Institute (DRI) is a recognized world leader in basic and applied environmental research. Committed to scientific excellence and integrity, DRI faculty, students who work alongside them, and staff have developed scientific knowledge and innovative technologies in research projects around the globe. Since 1959, DRI’s research has advanced scientific knowledge on topics ranging from humans’ impact on the environment to the environment’s impact on humans. DRI’s impactful science and inspiring solutions support Nevada’s diverse economy, provide science-based educational opportunities, and inform policymakers, business leaders, and community members. With campuses in Las Vegas and Reno, DRI serves as the non-profit research arm of the Nevada System of Higher Education. For more information, please visit www.dri.edu.
About Southern Nevada Health District
The Southern Nevada Health District serves as the local public health authority for Clark County, Boulder City, Henderson, Las Vegas, Mesquite and North Las Vegas. The agency safeguards the public health of the community’s residents and visitors through innovative programs, regulations, and initiatives focused on protecting and promoting their health and well-being. More information about the Health District, its programs, services, and the regulatory oversight it provides is available at www.SNHD.info. Follow the Health District on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.